
- #Undelete software linux how to#
- #Undelete software linux install#
- #Undelete software linux full#
- #Undelete software linux software#
#Undelete software linux software#
With so many great NTFS undelete software applications available today, you might think that selecting the best one would be difficult.

Sometimes, Scalpel restores parts of the file. $ sudo scalpel /dev/sdb1 -o recovered_files1
#Undelete software linux full#
Next, run the full Scalpel command, and in the output folder, you will see the recovered files. The file formats you uncomment, Scalpel will search for it. This configuration file is usually located at the following location: /etc/scalpel/nfĪnd you can open it with your favorite text editor, and there you will only have to uncomment the lines to define the file formats to search. Note that Scalpel will create the output directory itself.īut how does Scapel know which files to recover? Well, that is defined in the application configuration file.
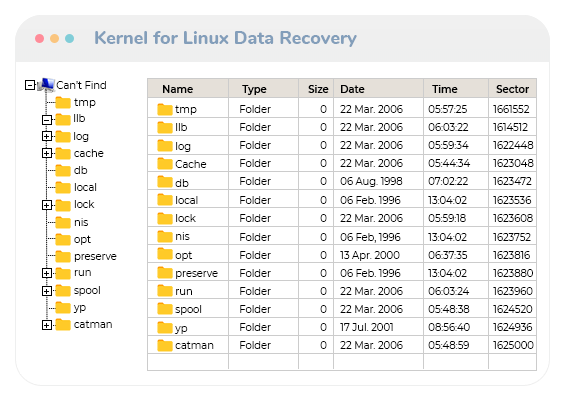
The output_folder specifies where scapel will place all recovered files. The fastest and easiest way to use Scapel is as follows: $ scalpel -o Therefore, its installation is reduced to the use of the terminal and the package manager of the distribution. Like TestDisk, it is available in the official repositories of most Linux distributions. It tries to extract headers and footers of files and tries to guess the entire file structure using some well-designed algorithms. Scalpel carves files without the help of filesystems. In this sense, it emerges as an alternative to consider. It is well known for its speed and efficiency. Scapel is another open-source tool that allows you to recover files from formatted drives, overwritten files, and even damaged drives. Recover overwritten files (Using Scalpel) All this thanks to the fact that Ext4 is a community and open source file system. If I wanted to recover the deleted files from a folder called files, the command would be similar to this one: $ sudo ext4magic /dev/sdb1 -r -d files
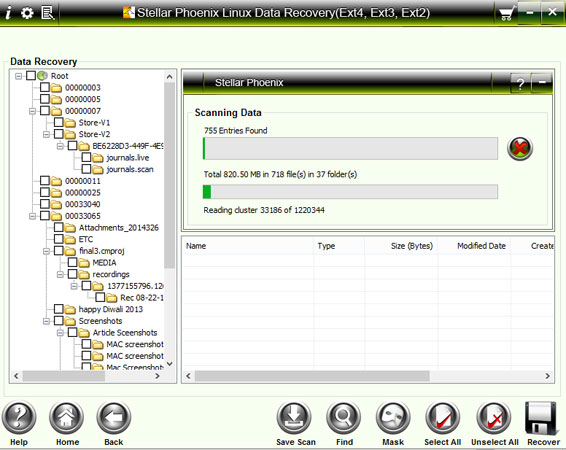
The most basic syntax of the application is the following: $ sudo ext4magic -f -r -d This application is also quite simple to use. In this particular case, sda is the partition we want to recover.Īnother alternative way to recover deleted files on a disk with an Ext4 file system is to use Ext4magic. Next, the disks or partitions recognized by the system will be scanned. If you don’t want a log file, select the No Log option. If you want to create one, choose the create option and press Enter. Next, you have the option to create a new file for the logs. If the clusters have not been overwritten, TestDisk can recover the files.įirst, start the application like this: $ testdisk
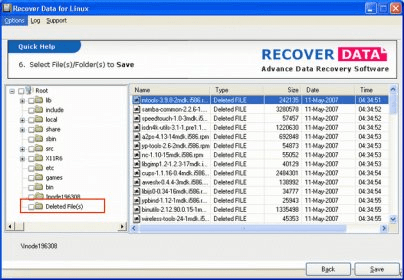
When you delete a file, the list of clusters occupied by the file is deleted, marking those sectors available for the use. These are the most popular partition tables.Īlso, it supports many file systems such as NTFS, EXT4, and other nonpopular file systems such as BeOS and ReiserFS. On the other hand, the application is cross-platform and supports a large number of partition tables such as Intel, MSDOS, and Mac. Most Linux distributions such as Debian and Ubuntu comes with TestDisk. Testdisk is a powerful partition analysis and data recovery utility.
#Undelete software linux how to#
However, how to recover files from those deleted partitions? For this, we need to recover the partition using a tool called TestDisk.
#Undelete software linux install#
Often, Linux users frequently install several systems at the same time, and they may delete a partition by mistake during the installation process.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
